Why?
So, In organizations, we have multiple AWS services/resources running in their environment and at times people forget to stop the unused resources/services and they go unused. And DevOps is all about optimizing the factors that support efficient development.
In the real-world DevOps scenario, The AWS Resource Tracker script is widely used to provide an overview of the AWS resources being utilized within an environment.
It aims to help organizations monitor and manage their AWS resources effectively. The script utilizes the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) to fetch information about different AWS services, such as S3 buckets, EC2 instances, Lambda functions, and IAM users.
What we will get from this project?
By running the AWS Resource Tracker script, users can quickly obtain a list of S3 buckets, EC2 instances, Lambda functions, and IAM users associated with their AWS account.
This information can be valuable for various purposes, including auditing, inventory management, resource optimization, and security assessment.
Create an EC2 instance
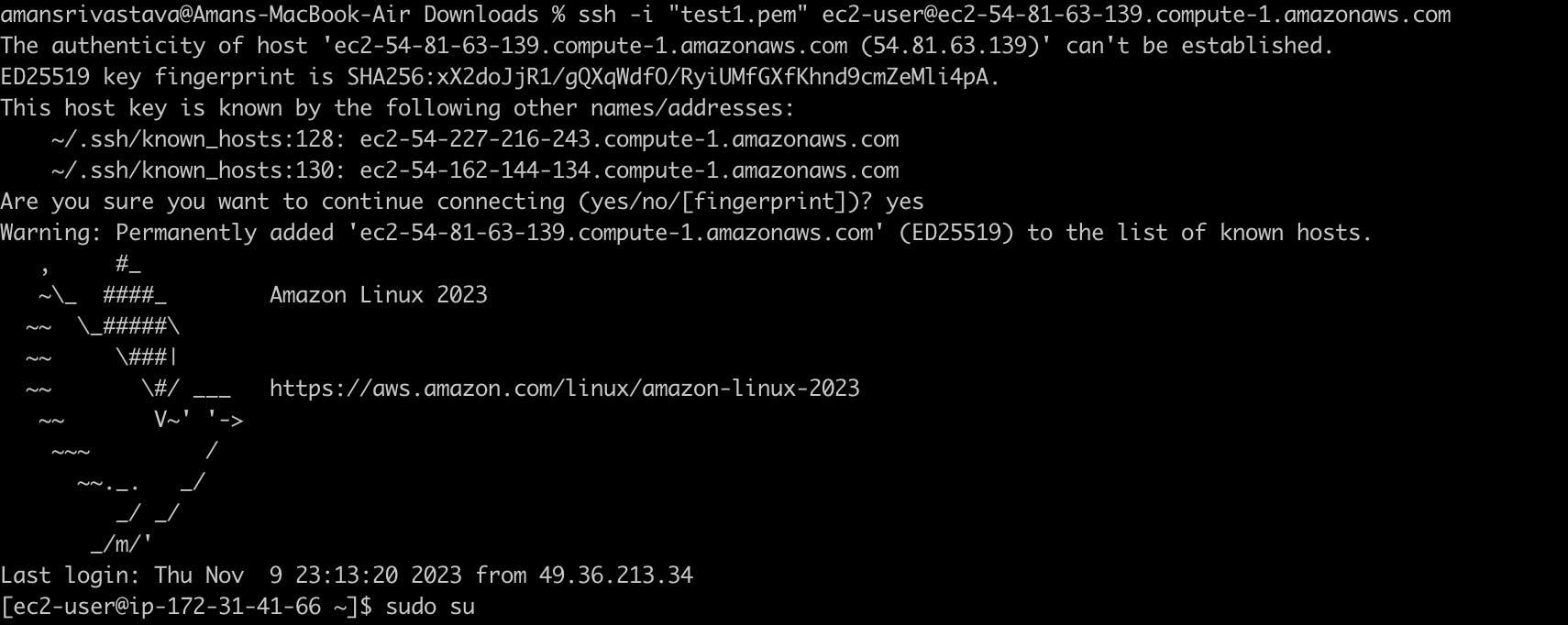
So, the first thing that we need to do is to create an EC2 instance in AWS. Please check out the below link to get started with EC2 instance creation. In this blog, we have covered EC2 creation and connecting it through SSH.
Once the EC2 instance is created, we will need to connect it through the SSH like below and then go to the root user with sudo su.
AWS CLI Configuration
Once we are connected install the AWS CLI with the below command.
sudo yum install aws-cli OR
sudo yum install aws-cli -y
aws --version - To check the version of CLI

Now we have to configure the AWS credentials and default configuration with the AWS CLI. To do this we need to run the below command and give the below information when prompted in CLI.
aws configure
AWS Access Key ID: This is your AWS access key, which is associated with an AWS IAM user. It is used to authenticate your CLI requests to AWS services.
AWS Secret Access Key: This is the corresponding secret key that goes along with the access key. It is used to authenticate your CLI requests.
Default Region: You can specify a default AWS region that the CLI should use for requests. If not specified, the CLI will use the region
us-east-1by default.Default Output Format: You can choose the default output format for the AWS CLI responses, such as JSON, text, or table. JSON is commonly used for machine-readable output.
To get your AWS Access and AWS Secret Access key, follow the below paths.
In the AWS console search for IAM.
Go to the users section on the left-hand side.
Select the user for whom you want to set AWS CLI
Now Scroll down and you will get an option to create an AWS Access key and an AWS Secret Access key.
Something like below :
The Script:
Now, that our set-up is completed, let's jump to create the scrips.
"aws_tracker" 35L, 553B 18,0-1 All
#########################
# Author: Your Name
# Date: 10/11/23
# Version: v1
#
# This script will report the AWS resource usage
########################
set -x
# AWS S3
# AWS EC2
# AWS Lambda
# AWS IAM Users
# list s3 buckets
echo "List of s3 buckets"
aws s3 ls
# list EC2 Instances
echo "List of ec2 instances"
aws ec2 describe-instances | jq '.Reservations[].Instances[].InstanceId'
# list lambda
echo "List of lambda functions"
aws lambda list-functions
# list IAM Users
echo "List of iam users"
aws iam list-users
It is a good convention to always provide your details so that it will make it easier for other developers to contribute if they want to ie, metadata.
The command
set -xis given here to debug the script, this will print the command that we are running and then print the output.The commands
aws s3 ls,aws lambda list-functionsandaws iam list-usersprint the information of the given statement.
aws ec2 describe instances | jq '.Reservations[].Instances[].InstanceId' will give you all the Instance IDs present in your aws in JSON format.Test the script:
Run the below command :
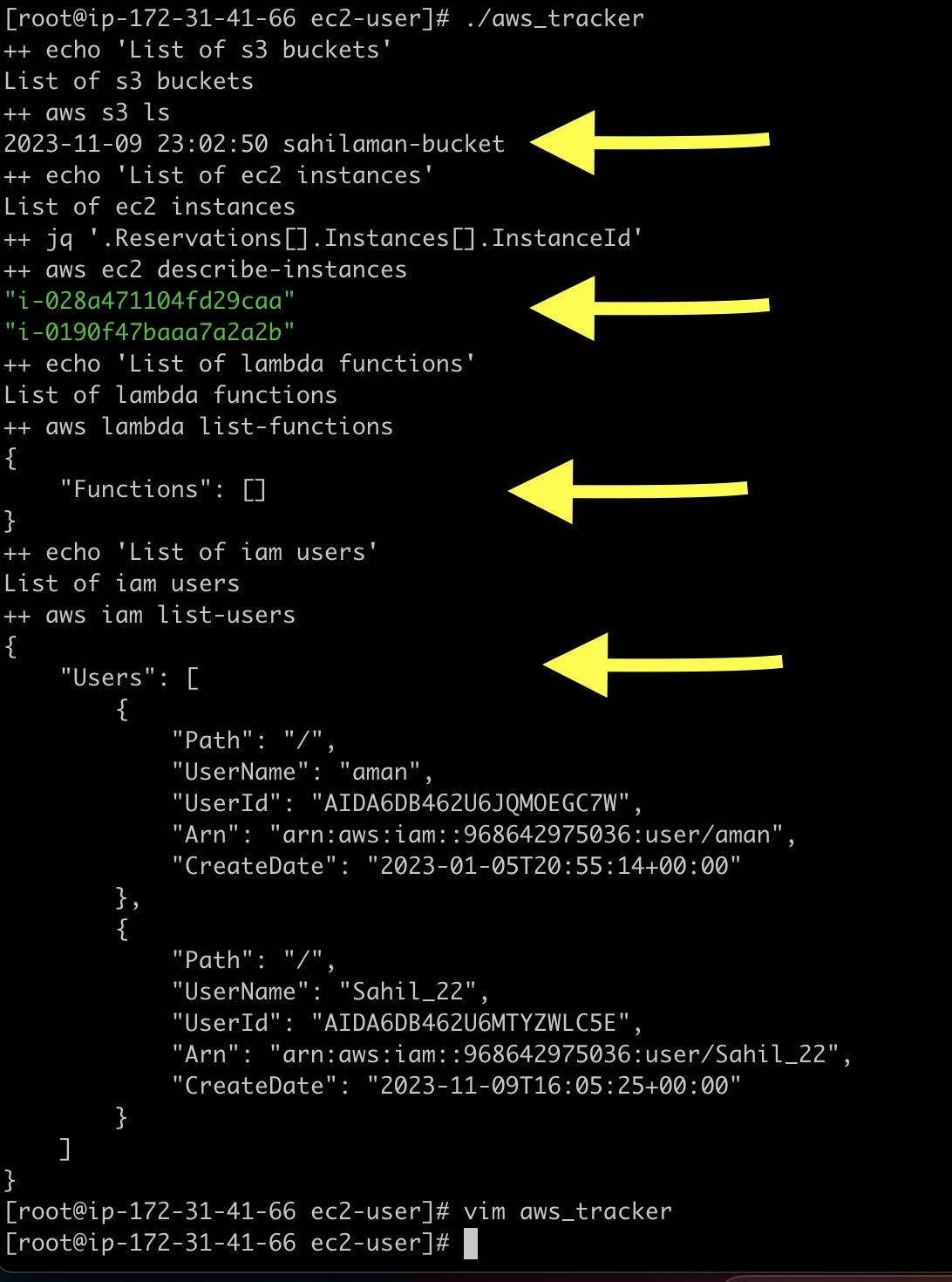
./aws_tracker
So, the script that I have created is getting 2 EC2 instances, 2 users one S3 bucket and there are no Lamda functions running.
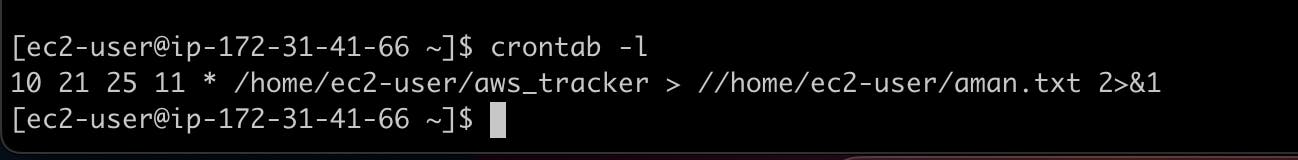
Schedule it with crontab:
Here's what each field in the cron schedule means:
0: Minute (0-59)3: Hour (0-23)``: Every day of the month
``: Every month
``: Every day of the week
Also with the below command, we can get the output of the script in a text format and get this saved in the file.
Here is the output of the command:
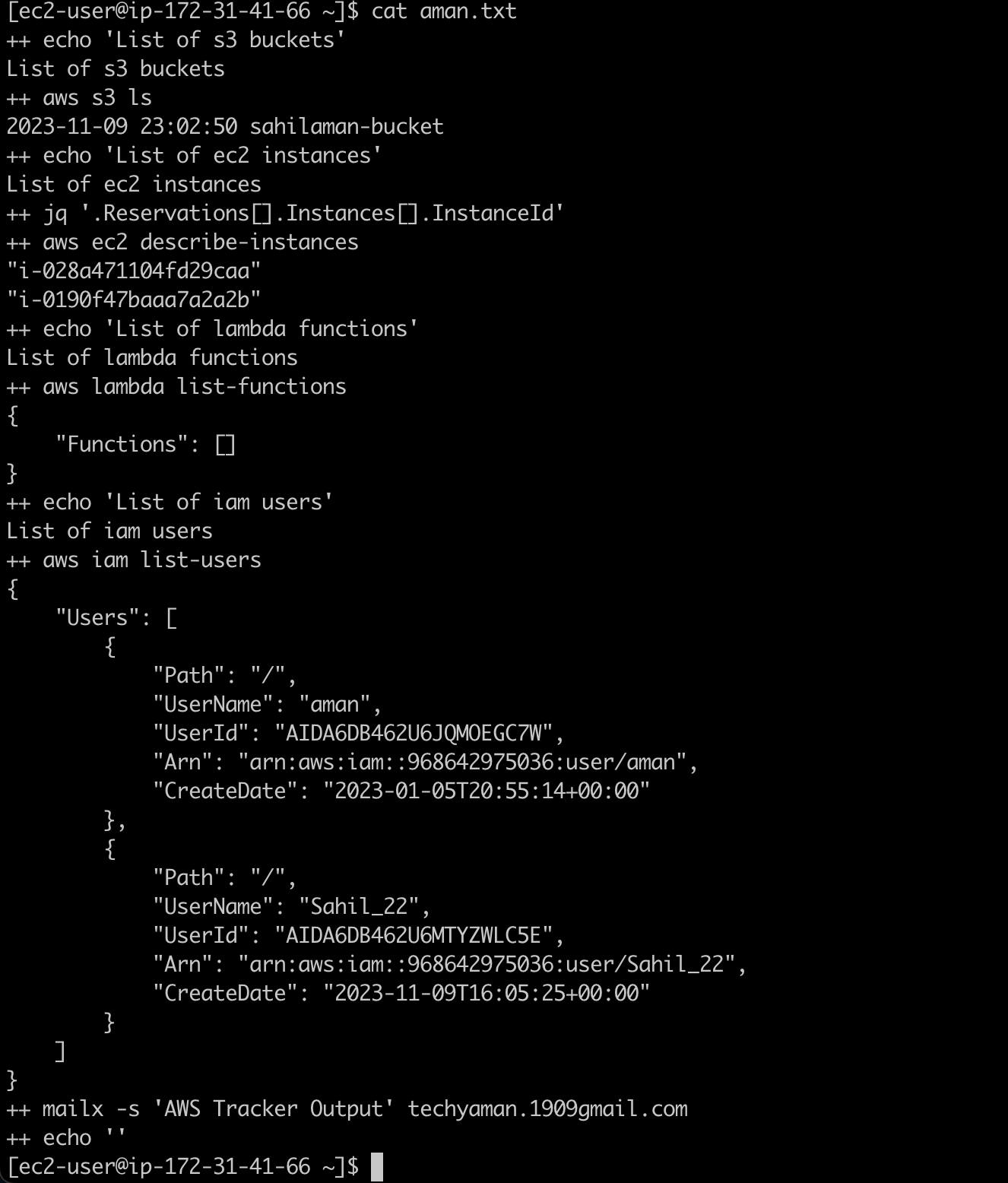
Hope this was helpful. Thank you for your time !!
Stay Connected, many more to come !!
Special thanks to Abhishek Veeramalla !!
