Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) is a web service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that offers resizable compute capacity in the cloud. It allows users to launch and manage virtual servers, known as EC2 instances, which can be configured with different operating systems, applications, and security settings.
EC2 stands for Elastic Compute Cloud and is a web service that provides secure, resizable compute capacity in the cloud.
EC2 allows users to rent virtual computers on which to run their applications.
EC2 instances can be launched in multiple sizes and configurations, allowing users to choose the instance type that best fits their needs.
EC2 instances can be launched in multiple regions and availability zones, allowing users to deploy their applications in multiple locations for increased availability and scalability.
EC2 instances can be launched with a variety of operating systems, including Windows, Linux, MacOS, Amazon Linux AWS and Unix.
EC2 instances can be launched with a variety of storage options, including Amazon EBS, Amazon S3, and Amazon Glacier.
EC2 instances can be launched with a variety of networking options, including Amazon VPC, Amazon Direct Connect, and Amazon Route 53.
EC2 instances can be launched with a variety of security options, including Amazon Security Groups, Amazon IAM roles, and Amazon CloudWatch.
EC2 instances can be launched with a variety of monitoring and logging options, including Amazon CloudWatch, Amazon CloudTrail, and Amazon CloudFormation.
Access reliable, scalable infrastructure on demand. Scale capacity within minutes with an SLA commitment of 99.99% availability.
Provide secure computing for your applications. Security is built into the foundation of Amazon EC2 with the AWS Nitro System.
Optimize performance and cost with flexible options like AWS Graviton-based instances, Amazon EC2 Spot instances, and AWS Savings Plans.
Typical use cases of AWS EC2 include:
Deliver secure, reliable, high-performance, and cost-effective computing infrastructure to meet demanding business needs.
Access the on-demand infrastructure and capacity you need to run HPC applications faster and cost-effectively.
Access environments in minutes, dynamically scale capacity as needed, and benefit from AWS’s pay-as-you-go pricing.
Deliver the broadest choice of computing, networking (up to 400 Gbps), and storage services purpose-built to optimize the price performance for ML projects
Host a variety of software from simple websites to enterprise-grade web applications on an on-demand infrastructure. Easy to lift and shift from on-premises since you have full control of the operating system. Spot pricing can help save up to 80-90% on hosting costs.
Create fault-tolerant architecture with auto-scaling and load-balancing options.
If you need heavy computation and GPU power for deep learning/ machine learning, choose EC2 accelerated computing instances.
EC2 Instance Types

General purpose:
A general purpose instance is a type of cloud computing instance that is designed to provide a balance of computing, memory, and storage resources for a wide variety of workloads. General-purpose instances are typically used for web and application servers, development and test environments, and small to medium databases.
For example, Amazon EC2 offers a variety of general-purpose instances, such as the M5, M4, and T2 instances. The M5 instances are designed for general-purpose workloads, such as web and application servers, development and test environments, and small to medium databases. The M4 instances are designed for memory-intensive workloads, such as in-memory databases, distributed web scale in-memory caches, and real-time big data analytics. The T2 instances are designed for burstable performance, such as web servers, developer environments, and small databases.
Compute optimized:
Compute Optimized Instance in AWS is a type of virtual machine (VM) that is designed to provide high-performance computing (HPC) capabilities. These instances are optimized for compute-intensive workloads such as high-performance computing (HPC), machine learning, and data processing. Compute Optimized Instances are designed to provide the highest performance for applications that require a lot of computing power.
Compute Optimized Instances are available in a variety of sizes and configurations, including the C4, C5, and C6g instances. These instances are designed to provide the highest performance for applications that require a lot of computing power. They are also cost-effective, as they are priced lower than other instance types.
For example, if you are running a machine learning application that requires a lot of computing power, you can use a Compute Optimized Instance to get the best performance. Compute Optimized Instances are also ideal for applications that require a lot of memory, such as databases and in-memory analytics.
Memory-optimized:
Memory Optimized Instance in AWS is a type of virtual machine (VM) that is designed to provide high-performance computing power for applications that require a large amount of memory. These instances are optimized for memory-intensive workloads such as high-performance databases, distributed caching, in-memory analytics, and other memory-intensive applications.
Memory Optimized Instance in AWS comes in a variety of sizes and configurations. The most common types are the R5, R4, and X1e instances.
For example, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) Memory Optimized Instances are designed to provide high-performance computing power for applications that require a large amount of memory. These instances are optimized for memory-intensive workloads such as high-performance databases, distributed caching, in-memory analytics, and other memory-intensive applications. They are available in a variety of sizes, ranging from 2 GiB to 6 TiB of RAM, and feature up to 128 vCPUs. They also offer enhanced networking performance, with up to 25 Gbps of network bandwidth. Additionally, they are designed to provide low latency and high throughput for memory-intensive workloads.
Storage optimized:
Storage Optimized Instance in AWS is a type of instance that is designed to provide high-performance storage for applications that require low latency and high throughput. These instances are optimized for workloads that require high I/O performance, such as NoSQL databases, distributed file systems, and data warehousing.
Storage Optimized Instances are available in two types:
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) Optimized Instances: These instances are designed to provide high throughput and low latency access to EBS volumes. They are ideal for applications that require high I/O performance, such as NoSQL databases, distributed file systems, and data warehousing.
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) Optimized Instances: These instances are designed to provide high throughput and low latency access to EFS file systems. They are ideal for applications that require high I/O performance, such as web applications, media streaming, and content delivery networks.
For example, if you are running a NoSQL database on AWS, you can use a Storage Optimized Instance to provide high-performance storage for your database. The instance will be optimized for low latency and high throughput, allowing your database to run faster and more efficiently.
Accelerated computing:
Accelerated Computing Instances in AWS are a type of virtual machine (VM) that are designed to provide high-performance computing (HPC) capabilities. These instances are powered by hardware accelerators, such as Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) or Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs), to provide the necessary computing power for applications that require high performance.
For example, an AWS Accelerated Computing Instance can be used to run a deep learning application that requires a large amount of data processing. The instance can be configured with a GPU or FPGA to provide the necessary computing power to process the data quickly and efficiently. Additionally, the instance can be configured with additional storage and networking capabilities to ensure that the application runs smoothly.
High Memory Instances:
These instances are a type of Amazon Web Services (AWS) virtual machines that are designed to provide a large amount of memory for applications that require it. These instances are ideal for applications that require a large amount of memory, such as databases, distributed caches, in-memory analytics, and other memory-intensive applications.
High Memory Instances come in a variety of sizes and configurations, allowing customers to choose the instance that best meets their needs. The most common types of High Memory Instances are the Amazon EC2 X1e, R5, and R6 instances.
EC2 Pricing Options:
On-Demand
Reserved
Spot-Instances
Dedicated Hosts
Let's explore each of them:
On-Demand:
It allows you to pay a fixed rate by the hour or even by the second with no commitment.
On-Demand is perfect for users who want low cost and flexibility of Amazon EC2 without any up-front investment or long-term commitment.
It is suitable for applications with short-term, spiky or unpredictable workloads that cannot be interrupted.
Reserved:
It is a way of making a reservation with Amazon or we can say that we make a contract with Amazon. The contract can be for 1 or 3 years in length.
In a Reserved instance, you are making a contract means you are paying some upfront, so it gives you a significant discount on the hourly charge for an instance.
It is useful for applications with steady state or predictable usage & used for those applications that require reserved capacity.
Users can make up-front payments to reduce their total computing costs. For example, if you pay all your upfronts and you do 3 years contract, then only you can get a maximum discount, and if you do not pay all upfronts and do one year contract then you will not be able to get as much discount as you can get If you do 3-year contract and pay all the upfronts.
Spot Instances:
It allows you to bid for a price whatever price you want for instance capacity, and provides better savings if your applications have flexible start and end times.
Spot Instances are useful for those applications that have flexible start and end times. And feasible at very low compute prices.
It is useful for those users who have an urgent need for large amounts of additional computing capacity.
EC2 Spot Instances provide fewer discounts as compared to On-Demand prices.
Spot Instances are used to optimize your costs on the AWS cloud and scale your application's throughput up to 10X.
EC2 Spot Instances will continue to exist until you terminate these instances.
Dedicated Hosts:
A dedicated host is a physical server with EC2 instance capacity which is fully dedicated to your use.
The physical EC2 server is the dedicated host that can help you to reduce costs by allowing you to use your existing server-bound software licenses. For example, Vmware, Oracle, SQL Server depending on the licenses that you can bring over to AWS and then they can use the Dedicated host.
Dedicated hosts are used to address compliance requirements and reduce costs by allowing you to use your existing server-bound server licenses.
It can be purchased as a Reservation for up to 70% off On-Demand price.
Types of Reserved Instances:
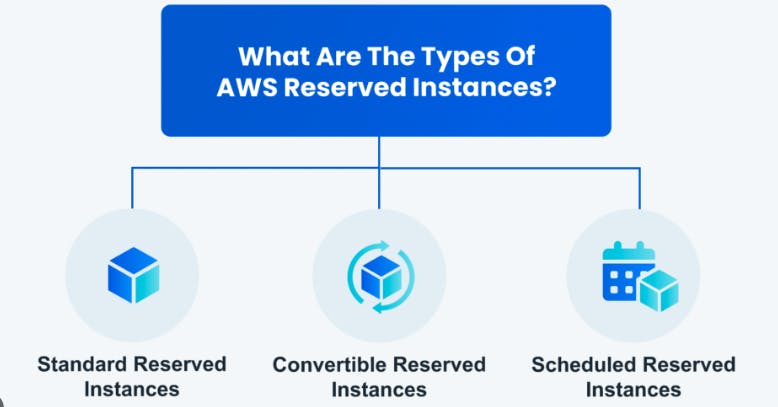
Standard Reserved Instances
It provides a discount of up to 75% off on demand. For example, you are paying all up-fronts for a 3-year contract.
It is useful when your Application is in a steady state.
Convertible Reserved Instances
It provides a discount of up to 54% off on demand.
It provides the feature that has the capability to change the attributes of RI as long as the exchange results in the creation of Reserved Instances of equal or greater value.
Like Standard Reserved Instances, it is also useful for steady-state applications.
Scheduled Reserved Instances
Scheduled Reserved Instances are available to launch within the specified time window you reserve.
It allows you to match your capacity reservation to a predictable recurring schedule that only requires a fraction of a day, a week, or a month.
Steps to start an EC2 Instance :
Log in to the AWS Management console.
Search for EC2 in the search bar.
On the left-hand side of your screen you will see instances, click on the instances.
Now, go to the top right-hand side, and you will see an option for Launch Instance, already highlighted with green color in the management console. Click on Launch Instances.
Now give a name for your machine under Name and tags and then select an Application and OS Image (Amazon Machine Image) for your machine based on your requirement. Always try to select Free tier OS to avoid billing, you can use OS based on your requirement too.
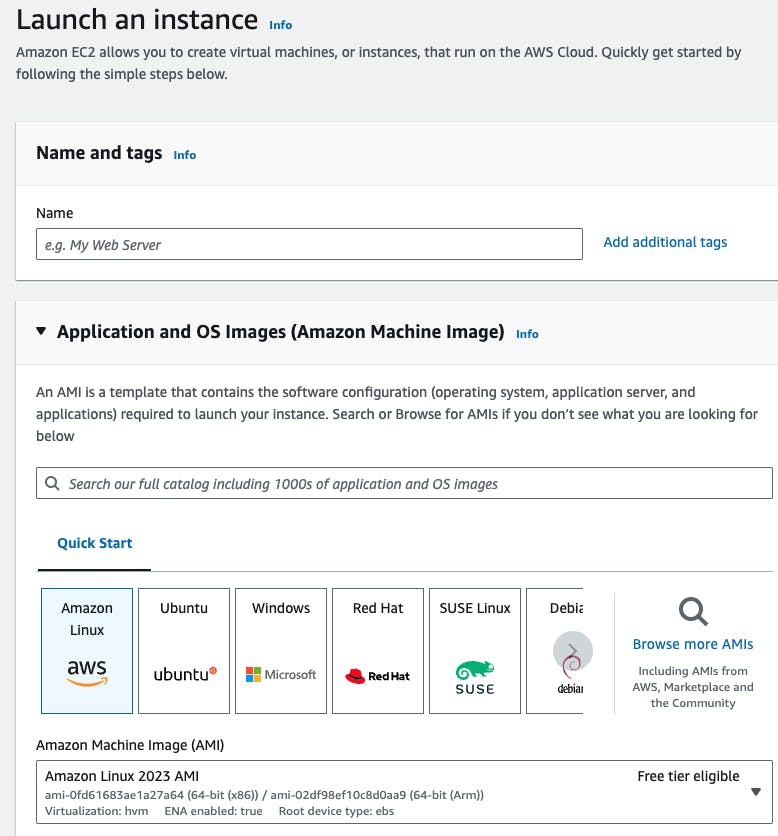
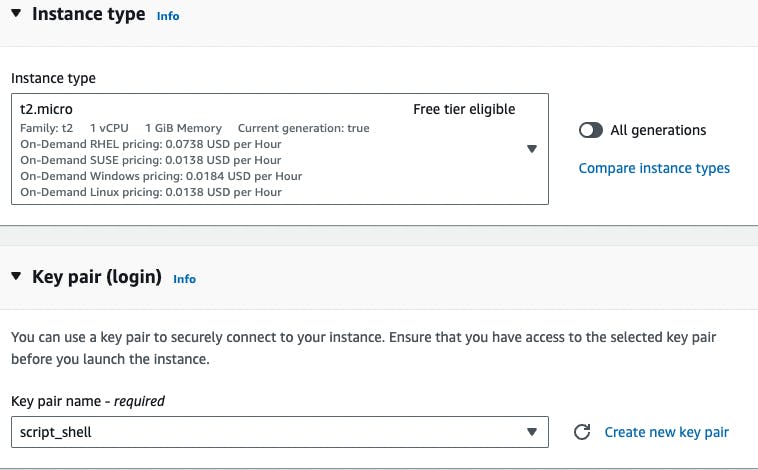
Now select the Instance type and Key pair (login), again for Instance type always choose free tier to avoid billing until and unless you don't have high load application to run on the server. Coming to the key pair, you will create a key pair from here and save it to your system.
Always try to save it to a folder where you can remember it as we can log in through the local system or jump host with the help of this pem file only. For jump hosts, you have to copy the poem file to the jump server.
At last, we have to configure the Network settings and Configure storage. We can create Security groups from here and allow access to different protocols and port no.
In storage, we can go up to 30 Gb for free but we have to use one VM at a time if we have given 30 GB to current VMs.
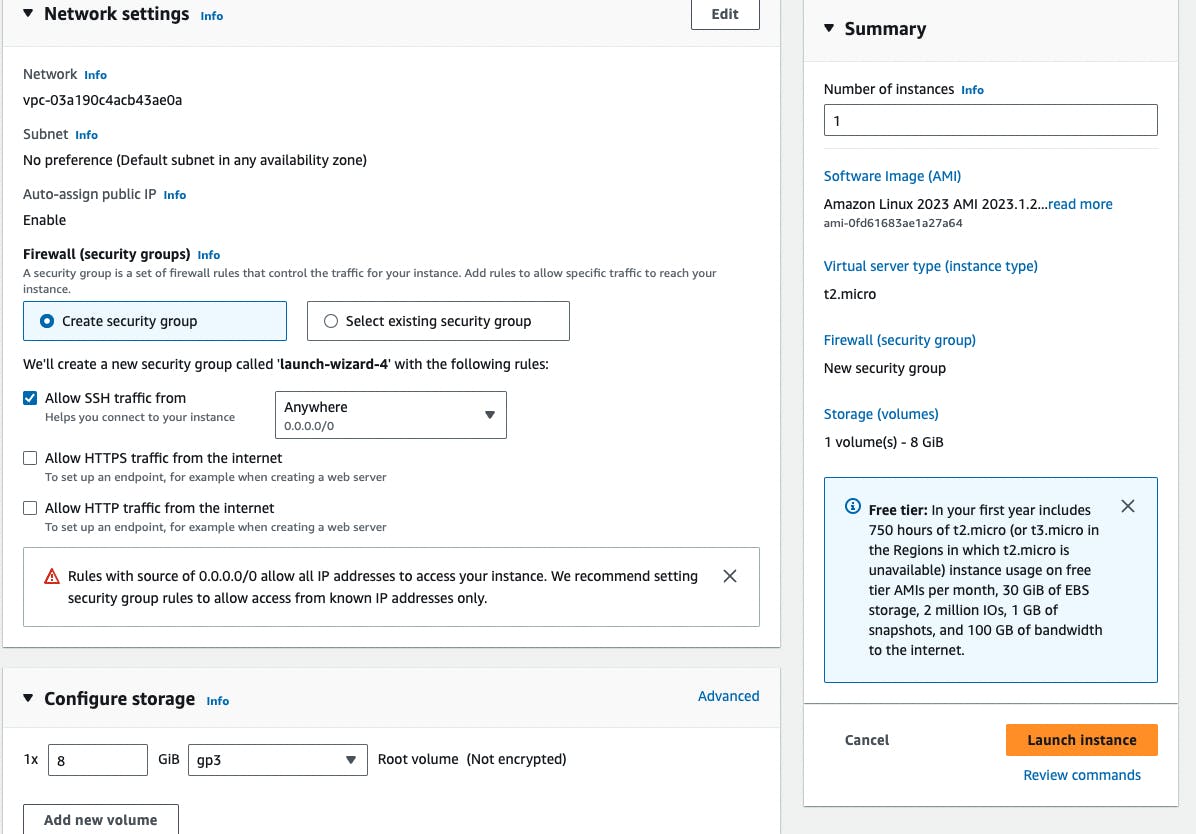
At last, we have to click on Launch Instance and our instance will be ready in a few secs or min.
Once the Instance configuration is done, click on the instance and then click on start instance.
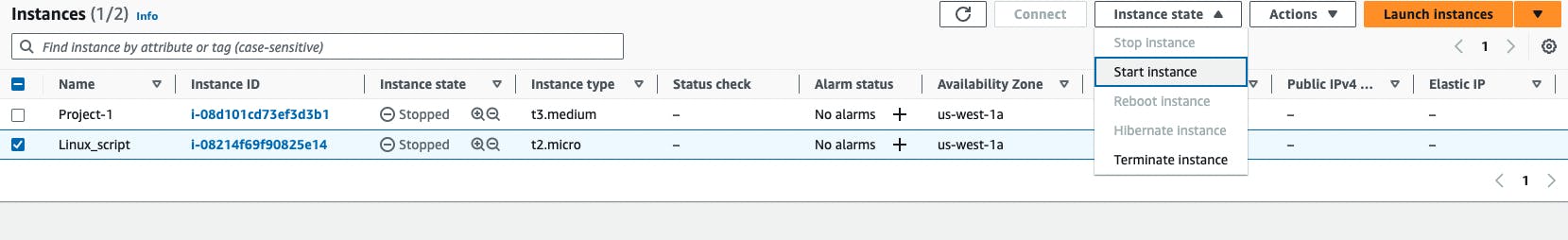
Once the Instance is up it will be running. Once it is running we can click on connect directly or through actions.
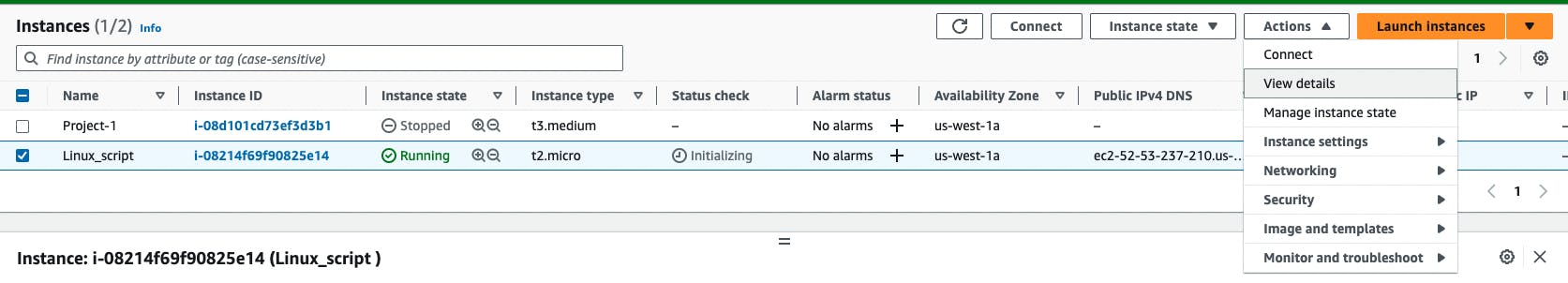
There are 4 options to connect to the EC2 instance, I generally use EC2 Instance connect or ssh.
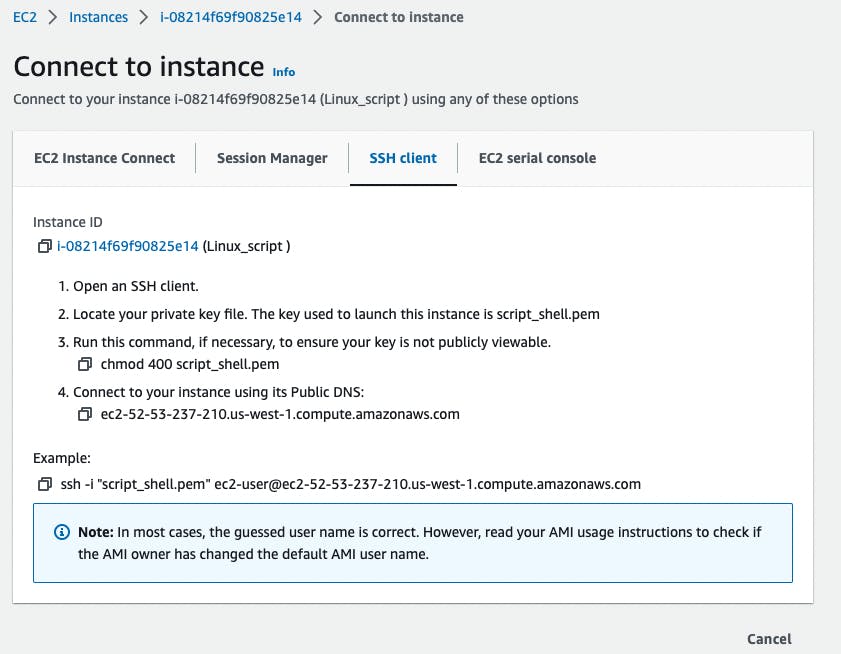
I have mentioned the pem file in the above steps, here we will use them through our local system console.
Command: ssh -i "script_shell.pem" ec2-user@ec2-52-53-237-210.us-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com
Note: Change the EC2 instance name according to your EC2 name, also this command is visible in the above picture as well. And the command will run only to the location where we have our pem file.
Here is the final output for the AWS EC2 instance on our local system.
Also, Explained the same in this short video about the creation of EC2 instances:
Hope this was helpful. Thank you for your time !!
Stay Connected, many more to come !!