Typically we want to replicate our containers i.e. our application for several reasons which include reliability, load balancing, and scaling. By having multiple versions of the application we prevent problems if one or more pods fail.
So, load balancing by having multiple versions of the containers enables us to easily send traffic to different instances to prevent overloading a single instance or not.
This is something that Kubernetes does but the box scaling benefit is that when the load becomes too much for several existing instances, Kubernetes enables it to easily scale up the application adding additional instances as needed. Replication is appropriate for numerous use cases which include microservices-based applications, cloud-native applications, or mobile backends.
Replication Controller:
The Replication Controller is one of the key features of Kubernetes, which is responsible for managing the pod lifecycle. It is responsible for making sure that the specified number of pod replicas are running at any point in time. It is used in times when one wants to make sure that the specified number of pods or at least one pod is running. It can bring up or down the specified no of pods.
It is a best practice to use the replication controller to manage the pod life cycle rather than creating a pod again and again.
Also, it helps us in load balancing and scaling the pods as the no of users increases.
Replication Controller Definition File:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ReplicationController
metadata:
name: myapp-rc
labels:
app: myapp
type: front-end
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: myapp-pod
labels:
app: myapp
type: front-end
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-container
image: nginx
replicas: 3
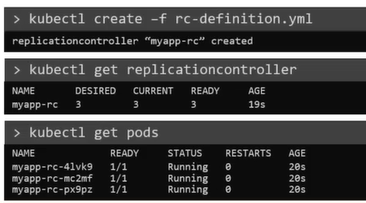
To create a replication controller
$ kubectl create -f rc-definition.yamlTo list all the replication controllers
$ kubectl get replicationcontrollerTo list pods that are launched by the replication controller
$ kubectl get pods
Replica sets:
Replica Sets are declared in the same way as Replication Controller except that they have more options for the selectors. The Selector is mandatory for Replica sets as match labels you can provide the pod labels to query the pods to match with the replica count.
Replicaset Definition File:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: myapp-replicaset
labels:
app: myapp
type: front-end
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: myapp-pod
labels:
app: myapp
type: front-end
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-container
image: nginx
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
type: front-end
Difference between Replication Controller & Replica Set:
| Replication Controller | Replica Set |
| The Replication Controller is the original form of replication in Kubernetes. | ReplicaSets are a higher-level API that gives the ability to easily run multiple instances of a given pod. |
| The Replication Controller uses equality-based selectors to manage the pods. | ReplicaSets Controller uses set-based selectors to manage the pods. |
| The rolling-update command works with Replication Controllers. | The rolling-update command won’t work with ReplicaSets. |
| Replica Controller is deprecated and replaced by ReplicaSets. | Deployments are recommended over ReplicaSets. |
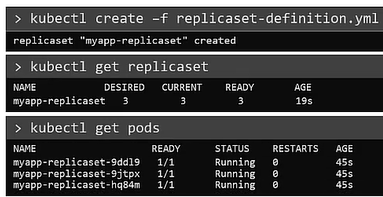
To Create the replicaset
$ kubectl create -f replicaset-definition.yamlTo list all the replicaset
$ kubectl get replicasetTo list pods that are launched by the replicaset
$ kubectl get pods
NOTE:
How does the replicaset would know which pod to montitor as there would be multiple pods in the cluster........??
Here comes the role of labels to solve this, we can label our replicaset to make it differ from the other pods. This can be done under the selectors section while creating the yaml definition file.
Selectors will select the labels that we will assign.
How to scale replicaset:
There are multiple ways to scale replicaset
- The first way is to update the number of replicas in the replicaset-definition.yaml definition file. E.g replicas: 6 and then run
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: myapp-replicaset
labels:
app: myapp
type: front-end
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: myapp-pod
labels:
app: myapp
type: front-end
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-container
image: nginx
replicas: 6
selector:
matchLabels:
type: front-end
$ kubectl apply -f replicaset-definition.yaml
2. The second way is to use kubectl scale command.
$ kubectl scale --replicas=6 -f replicaset-definition.yaml
3. The third way is to use kubectl scale command with type and name
$ kubectl scale --replicas=6 replicaset myapp-replicaset
Hope this was helpful. Thank you for your time !!
Stay Connected, many more to come !!