Kubernetes, often abbreviated as K8s, is a powerful tool for managing containerized applications. It uses a distributed architecture that relies on several key components working in harmony to deliver a seamless container orchestration experience. In this blog, we'll explore the core components and their roles within the Kubernetes ecosystem.

Let's now explore each of its components separately:
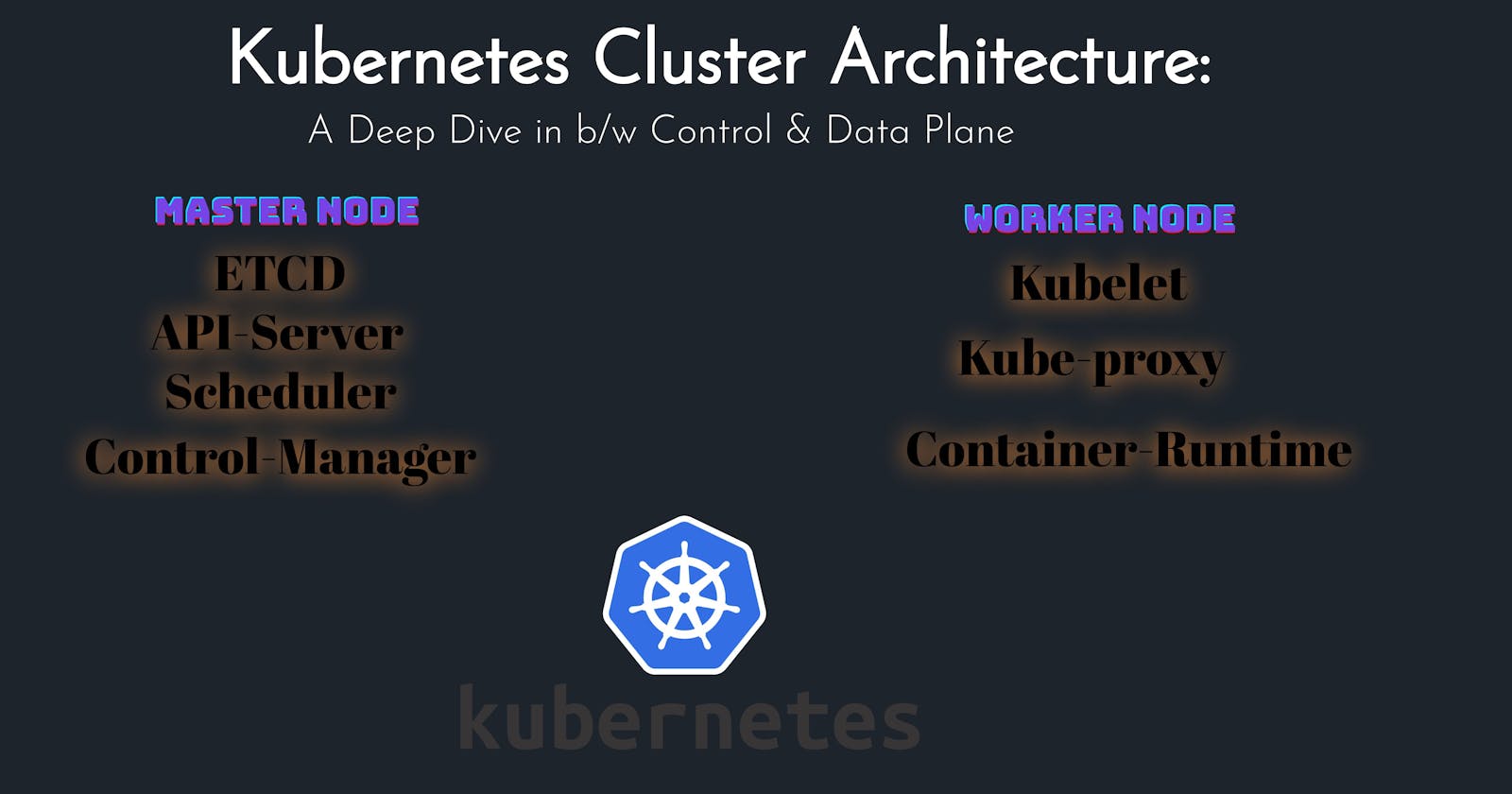
So we have a Kubernetes Master node and 2 worker nodes. The Master node has the responsibility of the etcd, API server, Kube scheduler, and Controller-Manager, On the other Worker node has the responsibility of Kubelet and Kube-proxy.
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
It provides a container-centric infrastructure, abstracting the underlying infrastructure complexity.
etcd 🗄️:
etcd is a distributed key-value store used by Kubernetes to store configuration data and cluster state.
It ensures consistent and highly available storage, making it a critical component for maintaining cluster health.
Kube API Server 🌐:
The Kubernetes API server is the entry point for all interactions with the cluster.
It validates and processes REST requests, enforces policies, and communicates with other components to manage the cluster.
Controller Manager 🛠️:
The Controller Manager includes various controllers that regulate the desired state of resources in the cluster.
It ensures that the actual state converges towards the desired state, managing tasks like scaling and maintaining pod replicas.
Kube Scheduler 📅:
The Kubernetes Scheduler assigns work (pods) to nodes in the cluster.
It considers factors like resource requirements, node capacity, and user-defined constraints to make optimal placement decisions.
It decides where your applications should run within the cluster based on factors like available resources, constraints, and your specifications. It ensures efficient resource utilization.
Kubelet 🌱:
Kubelet is responsible for node-level operations and manages pods on a node.
It communicates with the API server, ensures containers are running in a pod, and reports node health status.
Kube Proxy 🔗:
Kube Proxy is a network proxy that maintains network rules on nodes.
It facilitates communication to services within the cluster and ensures load balancing and routing of traffic to the appropriate pods.
Container-Runtime
Container runtime is the software responsible for running and managing containers on a host system. It executes containerized applications, provides resource isolation, and ensures security.
Imagine you have a container image containing a web application. When you run this container, the container runtime takes care of starting the web application, managing its resources (CPU, memory), and isolating it from other containers and the host system. It's like a conductor ensuring the application runs smoothly within its isolated environment.
Hope this was helpful. Thank you for your time !!
Stay Connected, many more to come !!
Also, please check out my YouTube channel, more content is to be delivered here.