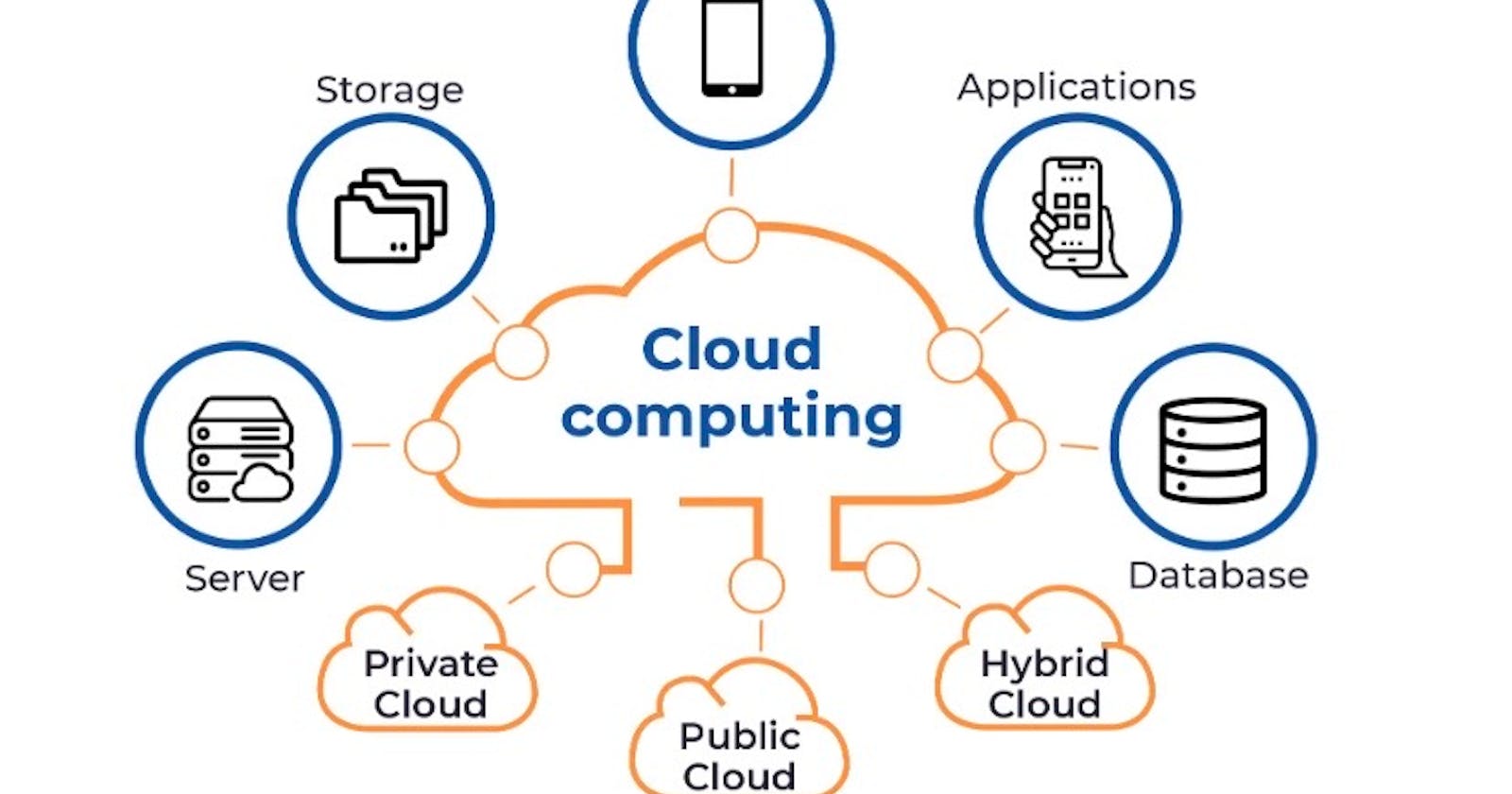
What is Cloud?
Let's start from basic, it's nothing but just a Datacenter which has servers, Storage, backup devices, Database servers, routers, Networks and switches. All are connected in a very big DC. We as cloud providers just take a part of them and give to our customers as a service. In this, the customer is free as he has no physical devices which helps them in cost cutting. This gives organizations the flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness they need and the services when they need.
Private vs Public Cloud !!
For Private vs Public cloud, The choice will depend on unique organizational requirements, such as security concerns, compliance standards, data sensitivity, budget, and scalability requirements. Both private and public clouds have their advantages. Many businesses use a hybrid cloud strategy, using the benefits of both private and public clouds to build a flexible and well-balanced IT architecture.
Private Cloud:
Enhanced Security and Control: Private Cloud provides organizations with exclusive control over security measures, enabling them to implement stringent security protocols and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Customization and Tailored Solutions: Private Cloud offers a higher degree of customization, allowing organizations to design and configure the cloud environment to meet their specific requirements, applications, and workflows.
Performance and Resource Allocation: With a Private Cloud, organizations have dedicated resources and can allocate them based on their workload demands, ensuring consistent performance and optimal resource utilization.
Data Privacy and Confidentiality: Private Cloud offers an added layer of data privacy and confidentiality as organizations have full control over their data and can ensure it remains within their infrastructure, minimizing exposure to external threats.
Flexibility and Scalability: Private Cloud provides organizations with the flexibility to scale resources up or down according to their needs, enabling seamless expansion or contraction of IT infrastructure as business requirements evolve.
Public Cloud:
Cost-Efficiency: Public Cloud eliminates the need for upfront infrastructure investment and ongoing maintenance costs. Organizations can leverage the pay-as-you-go model, paying only for the resources they consume, resulting in potential cost savings.
Global Reach and Accessibility: Public Cloud providers have a widespread infrastructure, enabling organizations to deploy their applications and services globally, reaching a broader audience and ensuring high availability and low-latency access.
Scalability and Elasticity: Public Cloud offers virtually unlimited scalability, allowing organizations to scale resources dynamically based on demand. This elasticity ensures businesses can rapidly respond to changing requirements without upfront planning or capacity constraints.
Reliability and Redundancy: Public Cloud providers have robust infrastructure and redundancy measures in place, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance. Organizations can benefit from the provider's expertise in maintaining reliable services.
Innovation and Breadth of Services: Public Cloud providers continually innovate and expand their service offerings. Organizations can leverage a vast array of services, such as AI, Big Data, analytics, and IoT, without the need for internal infrastructure investment or expertise.
AWS: Amazon Web Services
AWS is the most popular cloud provider, as he was the first to jump into the cloud business.
Amazon offers a complete cloud computing platform called AWS, which stands for Amazon Web Services. It provides an extensive array of scalable and on-demand services, such as processing power, storage, database management, networking, analytics, machine learning, and more.
The key motivation behind the creation of AWS was:
Enable Scalability
Increase Agility
Improve Cost Efficiency
Enhance Reliability & Security
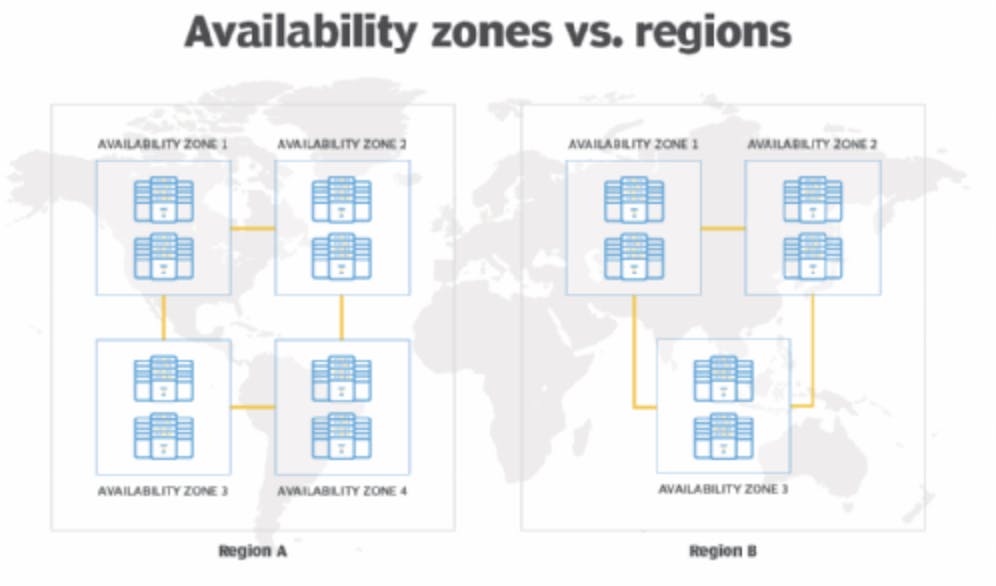
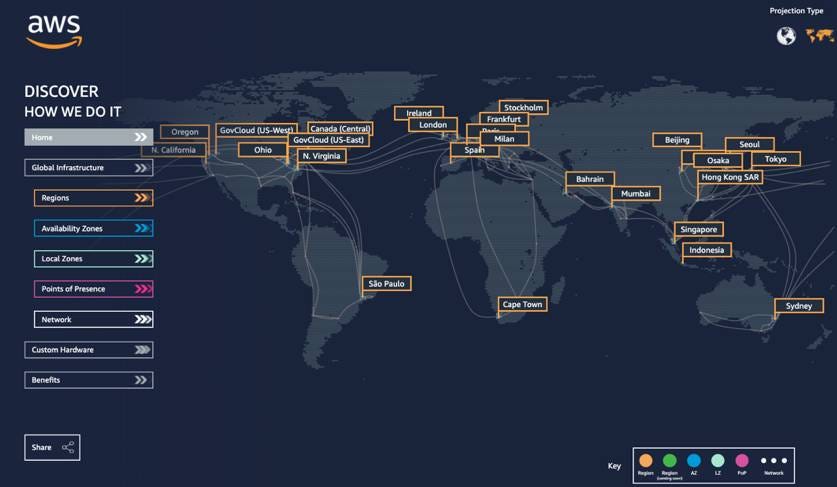
AWS Regions & Availability Zones:
AWS Regions are physical locations around the world where Amazon Web Services (AWS) has data centers. Each AWS Region is a separate geographic area with multiple Availability Zones. Regions are designed to provide low-latency access to AWS services and allow customers to choose the location that best suits their requirements. It is recommended to choose the nearest region for the customer to offer to avoid latency issues.
Availability Zones (AZs) are distinct data centers within an AWS Region. Each Availability Zone is a separate facility with redundant power, networking, and cooling. They are designed to provide high availability and fault tolerance by isolating infrastructure failures. AZs within a Region are interconnected through high-speed, low-latency links.
Link to Check RGs and AZs: https://aws.amazon.com/about-aws/global-infrastructure/regions_az/
Thank you !!!
Stay Connected, many more to come !!