What is VPN
Before we proceed with VPC, I want to give you an idea about VPN as well, this is used in organizations to have a secure connection between your local network and servers.

It enables secure communication and data transfer between your local network and resources in the remote network, such as an AWS VPC.
VPN is commonly used to connect on-premises networks to a VPC, allowing access to AWS resources securely.
AWS VPC provides the networking infrastructure within the AWS cloud, allowing you to create isolated environments and manage resources.
VPN can be used to establish a secure connection between your local network and the VPC, extending your network's reach into the AWS environment.
WS VPC is the virtual network infrastructure within AWS, while VPN is a technology that facilitates secure connectivity between your local network and resources in the VPC. VPN extends the reach of your local network to securely access AWS resources within the VPC.
What is AWS VPC?
AWS VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) is a virtual network that enables you to create isolated, secure environments within the AWS cloud. It allows you to define your network configuration, including IP address range, subnets, routing, and security settings, providing control and isolation for your AWS resources.
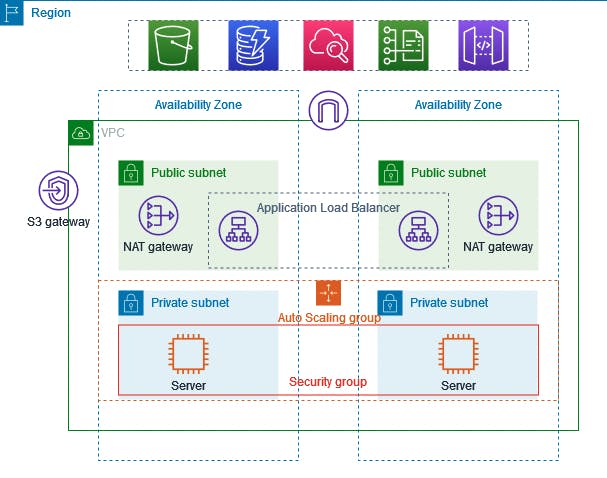
You can easily customize the network configuration for your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud. For example, you can create a public-facing subnet for web servers that can access the internet and can also place your backend system such as databases or application servers to a private-facing subnet.
You can provide multiple layers of security, including security groups and network access control lists, to help control access to Amazon EC2 instances in each subnet.
Uses of VPC:
Launch instances in a subnet of your choosing. We can choose our subnet address.
Deploy and manage EC2 instances within your VPC, providing secure and isolated environments for your applications.
Implement granular security controls using security groups and network ACLs to restrict inbound and outbound traffic at the instance and subnet levels.
We can create an internet gateway and attach it to our VPC.
We can assign custom IP address ranges in each subnet. And we can configure route tables between subnets.
We can use Load Balancing for instances inside VPC and auto-scaling to distribute the traffic and scale our applications.
VPC Peering:
VPC Peering connects two VPCs, enabling direct communication between them using private IP addresses. It allows resources in different VPCs to interact as if they are on the same network, without traversing the public internet.
We can peer VPCs with other AWS accounts as well as other VPCs in the same account.
Peering is in a star configuration, i.e., 1 VPC peers the other 4 VPCs.
It has no Transitive Peering. (Non-Transitive Peering means the networks that you want to connect are directly linked.)
You can peer between regions. Suppose you have one VPC in one region and another VPC in another region, then you can peer the VPCs between different regions.
Let's understand the example of non-transitive peering through an example.
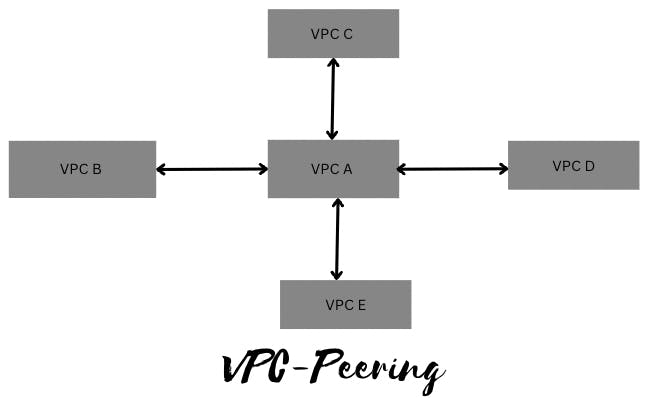
The above fig shows that all the VPCs are connected directly, let's dig a bit more, here it says that VPC B can communicate with VPC A but it can't communicate to VPC B through VPC A. It means that VPC B and VPC C can't talk as they are not directly linked. This is known as Non-Transitive Peering.
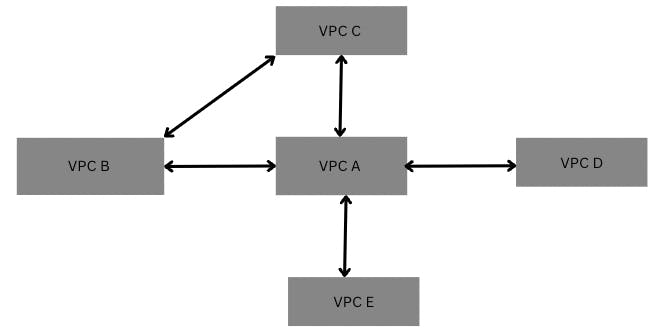
If we want to communicate to VPC B to VPC C we have to make a direct peering between them as shown in below fig.
Now Let's explore every term that we have used in VPC:
Subnets:
Subnets in AWS are segmented IP address ranges within a VPC that help organize resources and control network traffic by separating them into isolated network segments.
A subnet is a smaller portion of the network that typically includes all the machines in a certain area.
We can add as many as subnets we need in one availability zone. Each subnet must reside entirely within one availability zone.
The public subnets will be attached to Internet Gateway which enables Internet access.
The private subnets will not have internet access.
Every subnet which is presented in VPC must be associated with the routing table.
Public Subnet: Your network is exposed to the world and by default it gets internet.
Private Subnet: If you do not want to expose your server to the world that means no internet.
Internet gateway:
An Internet Gateway in AWS is a virtual gateway that allows traffic to flow between a VPC and the Internet, enabling communication with resources outside of the VPC. It acts as a bridge between the VPC and the internet.
One VPC can’t have more than one IGW
If resources are running in a certain VPC then IGW can not be detached from that particular VPC.
NAT Gateway:
NAT (Network Address Translation) in AWS allows private instances within a VPC to communicate with the internet by translating their private IP addresses to public IP addresses. It provides outbound internet access for instances in private subnets.
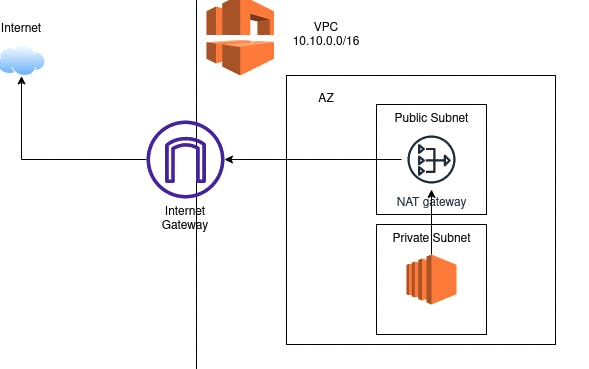
Let's dig a bit and understand it as a layman:
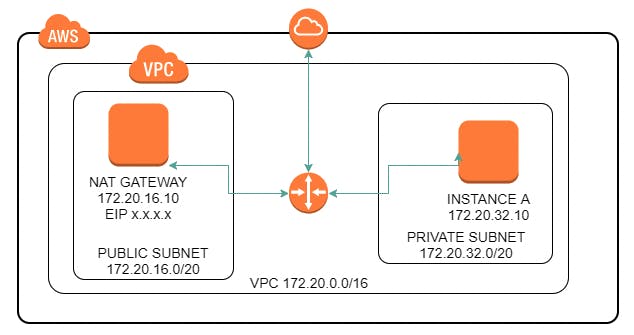
Suppose we have a Private subnet and an EC2 instance inside that wants to communicate to the outside internet. To make it secure from the outside world we have created a NAT gateway in a public subnet and associated a public IP to the NAT gateway.
So, when we request anything from the internet it goes to the NAT gateway, changes its IP from private to public and works as an immediate b/w internet and private subnet. And vice-versa happens when we get a response from the internet, NAT changes its IP to private and sends this to the requester i.e. EC2 in the private subnet.
IP Addressing:
IP addresses enable resources in your VPC to communicate with each other, and with resources over the internet.
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) notation is a way of representing an IP address and its network mask.
CIDR:
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a network management protocol used to dynamically assign an IP address to any device, or node on a network so it can communicate using IP. DHCP automates and centrally manages these configurations rather than requiring network administrators to manually assign IP addresses to all network devices. DHCP can be implemented on small local networks, as well as large enterprise networks.
For example, when a new EC2 instance is launched in a subnet, DHCP automatically assigns a unique IP address to that instance, facilitating seamless network connectivity without manual IP configuration.
We can also use elastic (static) IP as well in your VPC, After you bring the address range to AWS, it appears in your account as an address pool. You can create an Elastic IP address from your IPv4 address pool, and you can associate an IPv6 CIDR block from your IPv6 address pool with a VPC.
Route Table:
A routing table containing a set of rules, called routes, that are used to determine where network traffic from your subnet or gateway is directed.
When a network packet arrives at a Router, it determines the destination IP address of a received packet and makes the routing decision to send a packet to its destination. It determines how data flows between different subnets, ensuring efficient communication between classrooms, labs, and administrative offices.
Load Balancer:
A load balancer takes requests from clients and distributes them across targets in a target group.
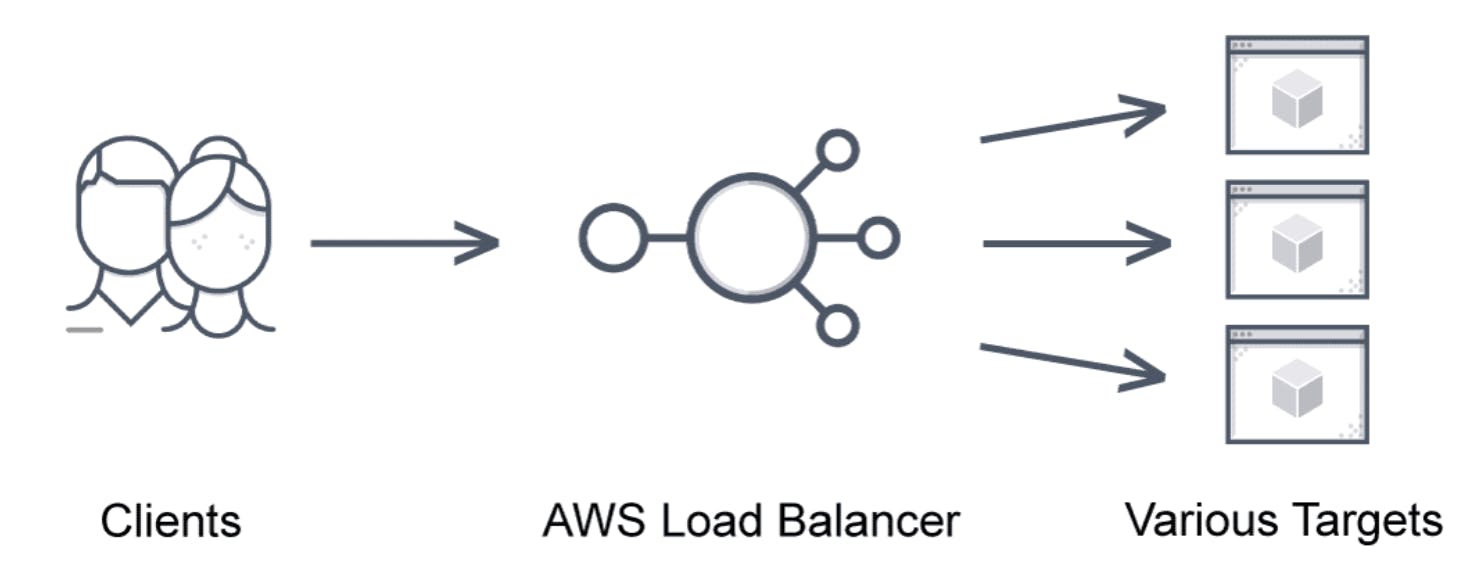
AWS load balancers accept incoming application traffic from clients and distribute it across various registered targets such as EC2 instances in multiple availability zones. The AWS application load balancer feature allows developers to route and configure incoming traffic in the AWS public cloud between end-users and applications.
A single point of contact for clients, the AWS elastic load balancer only routes to healthy instances and identifies unhealthy instances. Once the target is operational, the AWS load balancer algorithm resumes routing traffic to it.
AWS Load Balancer Types
There are four AWS load balancer types supported:
AWS Classic Load Balancer
AWS Network Load Balancer (NLB)
AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB)
AWS Gateway Load Balancer (GLB)
Auto Scaling group:
AWS Auto-Scaling is a mechanism that automatically permits you to increase or decrease your resources to meet demand based on custom-defined metrics and thresholds. Through Auto-scaling, it’s simple to set up application scaling for multiple resources across multiple services in minutes.
Benefits of Auto-Scaling
Setup Scaling Quickly
Make Smart Scaling Decisions
Automatically Maintain Performance
Pay Only For What You Need
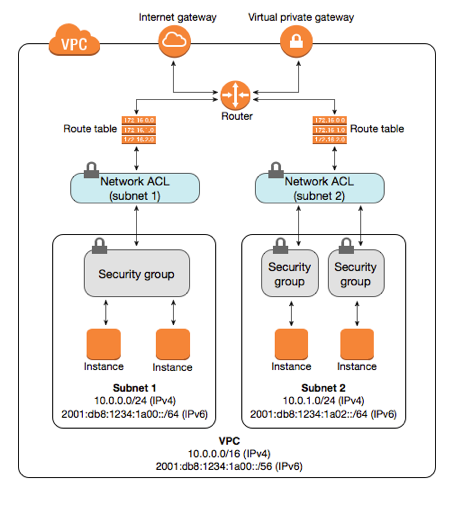
Security Groups:
In AWS, the Security group comprises a list of rules which are responsible for controlling the incoming and outgoing traffic to your compute resources such as EC2, RDS, lambda, etc.
Security groups in AWS act as virtual firewalls to compute resources such as EC2, ELB, RDS, etc. When you first launch an EC2 instance, you can associate it with one or more security groups.
Security Groups operate at the instance level and control traffic to and from individual EC2 instances.
NACL:
An optional layer of security that acts as a firewall for controlling traffic in and out of a subnet. You can associate multiple subnets with a single network ACL, but a subnet can be associated with only one network ACL at a time.
NACLs act as network-level firewalls within your VPC. They control inbound and outbound traffic for specific subnets, safeguarding against unauthorized access.
NACLs operate at the subnet level and control traffic in and out of a VPC
The below diagram will help you to understand the difference b/w SG and NACL:
In this comprehensive blog, I have covered everything that you need to know about VPC, will cover the practical implementation in our next blog.
Simple AWS VPC Creation:
Also, you can check out this video to have more clarity on VPC and its topics.
Hope this was helpful. Thank you for your time !!
Stay Connected, many more to come !!
